Image from: url
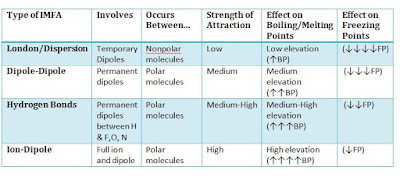
First, the intermolecular forces can divided into 5 categories. They are dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, iron-dipole forces and ionic bounding. If the intermolecular forces is strong enough to pull all molecules close together and shape a stable limited space with each molecules, this is what we known as solid. Oppositely, if the intermolecular forces is so weak that cannot attract each molecules together, then the molecules will separate with each other due to the repulsion and collisions. And this is what we called gases. The intermolecular forces of liquid is intervenient.
Image from: url
There are some other properties of substances relate to the intermolecular forces such as viscosity and surface tension. The viscosity will increase with stronger intermolecular forces and will decrease with weaker intermolecular forces. About surface tension, the molecular inner water can balance all the force from it's opposite directions. However, the molecules in the surface, they do not have a upward force to offset the force downward. Hence, if the weight of a lightly staff is equal to the downward force, this staff literally can stand on the water.

No comments:
Post a Comment